Portal:Mathematics
- አማርኛ
- العربية
- Avañe'ẽ
- Авар
- تۆرکجه
- বাংলা
- 閩南語 / Bân-lâm-gú
- Беларуская (тарашкевіца)
- Bikol Central
- Български
- Català
- Cebuano
- Čeština
- الدارجة
- Deutsch
- Eesti
- Ελληνικά
- Español
- فارسی
- Français
- Gĩkũyũ
- 한국어
- Hausa
- Հայերեն
- हिन्दी
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Interlingua
- Íslenska
- Italiano
- עברית
- ქართული
- Қазақша
- Kiswahili
- Kreyòl ayisyen
- Kurdî
- Latina
- Lietuvių
- Magyar
- Македонски
- Malti
- مصرى
- ဘာသာမန်
- Bahasa Melayu
- မြန်မာဘာသာ
- Nederlands
- 日本語
- Oʻzbekcha / ўзбекча
- ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
- پښتو
- Picard
- Polski
- Português
- Română
- Runa Simi
- Русский
- Shqip
- සිංහල
- سنڌي
- Slovenčina
- Soomaaliga
- کوردی
- Српски / srpski
- Suomi
- Svenska
- தமிழ்
- Taclḥit
- Татарча / tatarça
- တႆး
- ไทย
- Тоҷикӣ
- Türkçe
- Українська
- اردو
- Tiếng Việt
- 文言
- 吴语
- ייִדיש
- Yorùbá
- 粵語
- Zazaki
- 中文
- Batak Mandailing
- ⵜⴰⵎⴰⵣⵉⵖⵜ ⵜⴰⵏⴰⵡⴰⵢⵜ
Appearance
Portal maintenance status: (December 2018)
|
Wikipedia portal for content related to Mathematics
-
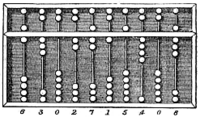
The Abacus, a ancient hand-operated mechanical wood-built calculator.
-
Portrait of Emmy Noether, around 1900.
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, theories and theorems that are developed and proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). (Full article...)
Featured articles
-
Image 1

The first 15,000 partial sums of 0 + 1 − 2 + 3 − 4 + ... The graph is situated with positive integers to the right and negative integers to the left.
In mathematics, 1 − 2 + 3 − 4 + ··· is an infinite series whose terms are the successive positive integers, given alternating signs. Using sigma summation notation the sum of the first m terms of the series can be expressed as
The infinite series diverges, meaning that its sequence of partial sums, (1, −1, 2, −2, 3, ...), does not tend towards any finite limit. Nonetheless, in the mid-18th century, Leonhard Euler wrote what he admitted to be a paradoxical equation:(Full article...)
-
Image 2

High-precision test of general relativity by the Cassini space probe (artist's impression): radio signals sent between the Earth and the probe (green wave) are delayed by the warping of spacetime (blue lines) due to the Sun's mass.
General relativity is a theory of gravitation developed by Albert Einstein between 1907 and 1915. The theory of general relativity says that the observed gravitational effect between masses results from their warping of spacetime.
By the beginning of the 20th century, Newton's law of universal gravitation had been accepted for more than two hundred years as a valid description of the gravitational force between masses. In Newton's model, gravity is the result of an attractive force between massive objects. Although even Newton was troubled by the unknown nature of that force, the basic framework was extremely successful at describing motion. (Full article...) -
Image 3In classical mechanics, the Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector (LRL vector) is a vector used chiefly to describe the shape and orientation of the orbit of one astronomical body around another, such as a binary star or a planet revolving around a star. For two bodies interacting by Newtonian gravity, the LRL vector is a constant of motion, meaning that it is the same no matter where it is calculated on the orbit; equivalently, the LRL vector is said to be conserved. More generally, the LRL vector is conserved in all problems in which two bodies interact by a central force that varies as the inverse square of the distance between them; such problems are called Kepler problems.
The hydrogen atom is a Kepler problem, since it comprises two charged particles interacting by Coulomb's law of electrostatics, another inverse-square central force. The LRL vector was essential in the first quantum mechanical derivation of the spectrum of the hydrogen atom, before the development of the Schrödinger equation. However, this approach is rarely used today. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Euclid's method for finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two starting lengths BA and DC, both defined to be multiples of a common "unit" length. The length DC being shorter, it is used to "measure" BA, but only once because the remainder EA is less than DC. EA now measures (twice) the shorter length DC, with remainder FC shorter than EA. Then FC measures (three times) length EA. Because there is no remainder, the process ends with FC being the GCD. On the right Nicomachus's example with numbers 49 and 21 resulting in their GCD of 7 (derived from Heath 1908:300).
In mathematics, the Euclidean algorithm, or Euclid's algorithm, is an efficient method for computing the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two integers, the largest number that divides them both without a remainder. It is named after the ancient Greek mathematician Euclid, who first described it in his Elements (c. 300 BC).
It is an example of an algorithm, a step-by-step procedure for performing a calculation according to well-defined rules,
and is one of the oldest algorithms in common use. It can be used to reduce fractions to their simplest form, and is a part of many other number-theoretic and cryptographic calculations.
The Euclidean algorithm is based on the principle that the greatest common divisor of two numbers does not change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. For example, 21 is the GCD of 252 and 105 (as 252 = 21 × 12 and 105 = 21 × 5), and the same number 21 is also the GCD of 105 and 252 − 105 = 147. Since this replacement reduces the larger of the two numbers, repeating this process gives successively smaller pairs of numbers until the two numbers become equal. When that occurs, that number is the GCD of the original two numbers. By reversing the steps or using the extended Euclidean algorithm, the GCD can be expressed as a linear combination of the two original numbers, that is the sum of the two numbers, each multiplied by an integer (for example, 21 = 5 × 105 + (−2) × 252). The fact that the GCD can always be expressed in this way is known as Bézout's identity. (Full article...) -
Image 5

The manipulations of the Rubik's Cube form the Rubik's Cube group.
In mathematics, a group is a set with a binary operation that satisfies the following constraints: the operation is associative, it has an identity element, and every element of the set has an inverse element.
Many mathematical structures are groups endowed with other properties. For example, the integers with the addition operation form an infinite group, which is generated by a single element called (these properties characterize the integers in a unique way). (Full article...)
-
Image 6
The Quine–Putnam indispensability argument is an argument in the philosophy of mathematics for the existence of abstract mathematical objects such as numbers and sets, a position known as mathematical platonism. It was named after the philosophers Willard Van Orman Quine and Hilary Putnam, and is one of the most important arguments in the philosophy of mathematics.
Although elements of the indispensability argument may have originated with thinkers such as Gottlob Frege and Kurt Gödel, Quine's development of the argument was unique for introducing to it a number of his philosophical positions such as naturalism, confirmational holism, and the criterion of ontological commitment. Putnam gave Quine's argument its first detailed formulation in his 1971 book Philosophy of Logic. He later came to disagree with various aspects of Quine's thinking, however, and formulated his own indispensability argument based on the no miracles argument in the philosophy of science. A standard form of the argument in contemporary philosophy is credited to Mark Colyvan; whilst being influenced by both Quine and Putnam, it differs in important ways from their formulations. It is presented in the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: (Full article...) -
Image 7

Logic studies valid forms of inference like modus ponens.
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure of arguments alone, independent of their topic and content. Informal logic is associated with informal fallacies, critical thinking, and argumentation theory. Informal logic examines arguments expressed in natural language whereas formal logic uses formal language. When used as a countable noun, the term "a logic" refers to a specific logical formal system that articulates a proof system. Logic plays a central role in many fields, such as philosophy, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics.
Logic studies arguments, which consist of a set of premises that leads to a conclusion. An example is the argument from the premises "it's Sunday" and "if it's Sunday then I don't have to work" leading to the conclusion "I don't have to work." Premises and conclusions express propositions or claims that can be true or false. An important feature of propositions is their internal structure. For example, complex propositions are made up of simpler propositions linked by logical vocabulary like(and) or
(if...then). Simple propositions also have parts, like "Sunday" or "work" in the example. The truth of a proposition usually depends on the meanings of all of its parts. However, this is not the case for logically true propositions. They are true only because of their logical structure independent of the specific meanings of the individual parts. (Full article...)
-
Image 8
Theodore John Kaczynski (/kəˈzɪnski/ ⓘ kə-ZIN-skee; May 22, 1942 – June 10, 2023), also known as the Unabomber (/ˈjuːnəbɒmər/ ⓘ YOO-nə-bom-ər), was an American mathematician and domestic terrorist. He was a mathematics prodigy, but abandoned his academic career in 1969 to pursue a reclusive primitive lifestyle.
Kaczynski murdered three people and injured 23 others between 1978 and 1995 in a nationwide mail bombing campaign against people he believed to be advancing modern technology and the destruction of the natural environment. He authored Industrial Society and Its Future, a 35,000-word manifesto and social critique opposing all forms of technology, rejecting leftism, and advocating a nature-centered form of anarchism. (Full article...) -
Image 9

Plots of logarithm functions, with three commonly used bases. The special points logb b = 1 are indicated by dotted lines, and all curves intersect in logb 1 = 0.
In mathematics, the logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, must be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the 3rd power: 1000 = 103 = 10 × 10 × 10. More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, written logb x, so log10 1000 = 3. As a single-variable function, the logarithm to base b is the inverse of exponentiation with base b.
The logarithm base 10 is called the decimal or common logarithm and is commonly used in science and engineering. The natural logarithm has the number e ≈ 2.718 as its base; its use is widespread in mathematics and physics because of its very simple derivative. The binary logarithm uses base 2 and is widely used in computer science, information theory, music theory, and photography. When the base is unambiguous from the context or irrelevant it is often omitted, and the logarithm is written log x. (Full article...) -
Image 10
Edward Wright (baptised 8 October 1561; died November 1615) was an English mathematician and cartographer noted for his book Certaine Errors in Navigation (1599; 2nd ed., 1610), which for the first time explained the mathematical basis of the Mercator projection by building on the works of Pedro Nunes, and set out a reference table giving the linear scale multiplication factor as a function of latitude, calculated for each minute of arc up to a latitude of 75°. This was in fact a table of values of the integral of the secant function, and was the essential step needed to make practical both the making and the navigational use of Mercator charts.
Wright was born at Garveston in Norfolk and educated at Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge, where he became a fellow from 1587 to 1596. In 1589 the college granted him leave after Elizabeth I requested that he carry out navigational studies with a raiding expedition organised by the Earl of Cumberland to the Azores to capture Spanish galleons. The expedition's route was the subject of the first map to be prepared according to Wright's projection, which was published in Certaine Errors in 1599. The same year, Wright created and published the first world map produced in England and the first to use the Mercator projection since Gerardus Mercator's original 1569 map. (Full article...) -
Image 11One of Molyneux's celestial globes, which is displayed in Middle Temple Library – from the frontispiece of the Hakluyt Society's 1889 reprint of A Learned Treatise of Globes, both Cœlestiall and Terrestriall, one of the English editions of Robert Hues' Latin work Tractatus de Globis (1594)
Emery Molyneux (/ˈɛməri ˈmɒlɪnoʊ/ EM-ər-ee MOL-in-oh; died June 1598) was an English Elizabethan maker of globes, mathematical instruments and ordnance. His terrestrial and celestial globes, first published in 1592, were the first to be made in England and the first to be made by an Englishman.
Molyneux was known as a mathematician and maker of mathematical instruments such as compasses and hourglasses. He became acquainted with many prominent men of the day, including the writer Richard Hakluyt and the mathematicians Robert Hues and Edward Wright. He also knew the explorers Thomas Cavendish, Francis Drake, Walter Raleigh and John Davis. Davis probably introduced Molyneux to his own patron, the London merchant William Sanderson, who largely financed the construction of the globes. When completed, the globes were presented to Elizabeth I. Larger globes were acquired by royalty, noblemen and academic institutions, while smaller ones were purchased as practical navigation aids for sailors and students. The globes were the first to be made in such a way that they were unaffected by the humidity at sea, and they came into general use on ships. (Full article...) -
Image 12
Amalie Emmy Noether (US: /ˈnʌtər/, UK: /ˈnɜːtə/; German: [ˈnøːtɐ]; 23 March 1882 – 14 April 1935) was a German mathematician who made many important contributions to abstract algebra. She also proved Noether's first and second theorems, which are fundamental in mathematical physics. Noether was described by Pavel Alexandrov, Albert Einstein, Jean Dieudonné, Hermann Weyl and Norbert Wiener as the most important woman in the history of mathematics. As one of the leading mathematicians of her time, she developed theories of rings, fields, and algebras. In physics, Noether's theorem explains the connection between symmetry and conservation laws.
Noether was born to a Jewish family in the Franconian town of Erlangen; her father was the mathematician Max Noether. She originally planned to teach French and English after passing the required examinations but instead studied mathematics at the University of Erlangen, where her father lectured. After completing her doctorate in 1907 under the supervision of Paul Gordan, she worked at the Mathematical Institute of Erlangen without pay for seven years. At the time, women were largely excluded from academic positions. In 1915, she was invited by David Hilbert and Felix Klein to join the mathematics department at the University of Göttingen, a world-renowned center of mathematical research. The philosophical faculty objected, however, and she spent four years lecturing under Hilbert's name. Her habilitation was approved in 1919, allowing her to obtain the rank of Privatdozent. (Full article...) -
Image 13Portrait by Jakob Emanuel Handmann, 1753
Leonhard Euler (/ˈɔɪlər/ OY-lər; German: [ˈleːɔnhaʁt ˈʔɔʏlɐ] ⓘ, Swiss Standard German: [ˈleɔnhard ˈɔʏlər]; 15 April 1707 – 18 September 1783) was a Swiss polymath who was active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, logician, geographer, and engineer. He founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made influential discoveries in many other branches of mathematics, such as analytic number theory, complex analysis, and infinitesimal calculus. He also introduced much of modern mathematical terminology and notation, including the notion of a mathematical function. He is known for his work in mechanics, fluid dynamics, optics, astronomy, and music theory. Euler has been called a "universal genius" who "was fully equipped with almost unlimited powers of imagination, intellectual gifts and extraordinary memory". He spent most of his adult life in Saint Petersburg, Russia, and in Berlin, then the capital of Prussia.
Euler is credited for popularizing the Greek letter(lowercase pi) to denote the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, as well as first using the notation
for the value of a function, the letter
to express the imaginary unit
, the Greek letter
(capital sigma) to express summations, the Greek letter
(capital delta) for finite differences, and lowercase letters to represent the sides of a triangle while representing the angles as capital letters. He gave the current definition of the constant
, the base of the natural logarithm, now known as Euler's number. Euler made contributions to applied mathematics and engineering, such as his study of ships which helped navigation, his three volumes on optics contributed to the design of microscopes and telescopes, and he studied the bending of beams and the critical load of columns. (Full article...)
-
Image 14A stamp of Zhang Heng issued by China Post in 1955
Zhang Heng (Chinese: 張衡; AD 78–139), formerly romanized Chang Heng, was a Chinese polymathic scientist and statesman who lived during the Eastern Han dynasty. Educated in the capital cities of Luoyang and Chang'an, he achieved success as an astronomer, mathematician, seismologist, hydraulic engineer, inventor, geographer, cartographer, ethnographer, artist, poet, philosopher, politician, and literary scholar.
Zhang Heng began his career as a minor civil servant in Nanyang. Eventually, he became Chief Astronomer, Prefect of the Majors for Official Carriages, and then Palace Attendant at the imperial court. His uncompromising stance on historical and calendrical issues led to his becoming a controversial figure, preventing him from rising to the status of Grand Historian. His political rivalry with the palace eunuchs during the reign of Emperor Shun (r. 125–144) led to his decision to retire from the central court to serve as an administrator of Hejian Kingdom in present-day Hebei. Zhang returned home to Nanyang for a short time, before being recalled to serve in the capital once more in 138. He died there a year later, in 139. (Full article...) -
Image 15Bust of Shen at the Beijing Ancient Observatory
Shen Kuo (Chinese: 沈括; 1031–1095) or Shen Gua, courtesy name Cunzhong (存中) and pseudonym Mengqi (now usually given as Mengxi) Weng (夢溪翁), was a Chinese polymath, scientist, and statesman of the Song dynasty (960–1279). Shen was a master in many fields of study including mathematics, optics, and horology. In his career as a civil servant, he became a finance minister, governmental state inspector, head official for the Bureau of Astronomy in the Song court, Assistant Minister of Imperial Hospitality, and also served as an academic chancellor. At court his political allegiance was to the Reformist faction known as the New Policies Group, headed by Chancellor Wang Anshi (1021–1085).
In his Dream Pool Essays or Dream Torrent Essays (夢溪筆談; Mengxi Bitan) of 1088, Shen was the first to describe the magnetic needle compass, which would be used for navigation (first described in Europe by Alexander Neckam in 1187). Shen discovered the concept of true north in terms of magnetic declination towards the north pole, with experimentation of suspended magnetic needles and "the improved meridian determined by Shen's [astronomical] measurement of the distance between the pole star and true north". This was the decisive step in human history to make compasses more useful for navigation, and may have been a concept unknown in Europe for another four hundred years (evidence of German sundials made circa 1450 show markings similar to Chinese geomancers' compasses in regard to declination). (Full article...)
Good articles
-
Image 1
Arnold Ephraim Ross (August 24, 1906 – September 25, 2002) was a mathematician and educator who founded the Ross Mathematics Program, a number theory summer program for gifted high school students. He was born in Chicago, but spent his youth in Odesa, Ukraine, where he studied with Samuil Shatunovsky. Ross returned to Chicago and enrolled in University of Chicago graduate coursework under E. H. Moore, despite his lack of formal academic training. He received his Ph.D. and married his wife, Bee, in 1931.
Ross taught at several institutions including St. Louis University before becoming chair of University of Notre Dame's mathematics department in 1946. He started a teacher training program in mathematics that evolved into the Ross Mathematics Program in 1957 with the addition of high school students. The program moved with him to Ohio State University when he became their department chair in 1963. Though forced to retire in 1976, Ross ran the summer program until 2000. He had worked with over 2,000 students during more than forty summers. (Full article...) -
Image 2

"The Gherkin", 30 St Mary Axe, London, completed 2003, is a parametrically designed solid of revolution.
Mathematics and architecture are related, since architecture, like some other arts, uses mathematics for several reasons. Apart from the mathematics needed when engineering buildings, architects use geometry: to define the spatial form of a building; from the Pythagoreans of the sixth century BC onwards, to create architectural forms considered harmonious, and thus to lay out buildings and their surroundings according to mathematical, aesthetic and sometimes religious principles; to decorate buildings with mathematical objects such as tessellations; and to meet environmental goals, such as to minimise wind speeds around the bases of tall buildings.
In ancient Egypt, ancient Greece, India, and the Islamic world, buildings including pyramids, temples, mosques, palaces and mausoleums were laid out with specific proportions for religious reasons. In Islamic architecture, geometric shapes and geometric tiling patterns are used to decorate buildings, both inside and outside. Some Hindu temples have a fractal-like structure where parts resemble the whole, conveying a message about the infinite in Hindu cosmology. In Chinese architecture, the tulou of Fujian province are circular, communal defensive structures. In the twenty-first century, mathematical ornamentation is again being used to cover public buildings. (Full article...) -
Image 3

Four opaque sets for a unit square. Upper left: its boundary, length 4. Upper right: Three sides, length 3. Lower left: a Steiner tree of the vertices, length . Lower right: the conjectured optimal solution, length
.
In discrete geometry, an opaque set is a system of curves or other set in the plane that blocks all lines of sight across a polygon, circle, or other shape. Opaque sets have also been called barriers, beam detectors, opaque covers, or (in cases where they have the form of a forest of line segments or other curves) opaque forests. Opaque sets were introduced by Stefan Mazurkiewicz in 1916, and the problem of minimizing their total length was posed by Frederick Bagemihl in 1959.
For instance, visibility through a unit square can be blocked by its four boundary edges, with length 4, but a shorter opaque forest blocks visibility across the square with length. It is unproven whether this is the shortest possible opaque set for the square, and for most other shapes this problem similarly remains unsolved. The shortest opaque set for any bounded convex set in the plane has length at most the perimeter of the set, and at least half the perimeter. For the square, a slightly stronger lower bound than half the perimeter is known. Another convex set whose opaque sets are commonly studied is the unit circle, for which the shortest connected opaque set has length
. Without the assumption of connectivity, the shortest opaque set for the circle has length at least
and at most
. (Full article...)
-
Image 4In number theory, a Wieferich prime is a prime number p such that p2 divides 2p − 1 − 1, therefore connecting these primes with Fermat's little theorem, which states that every odd prime p divides 2p − 1 − 1. Wieferich primes were first described by Arthur Wieferich in 1909 in works pertaining to Fermat's Last Theorem, at which time both of Fermat's theorems were already well known to mathematicians.
Since then, connections between Wieferich primes and various other topics in mathematics have been discovered, including other types of numbers and primes, such as Mersenne and Fermat numbers, specific types of pseudoprimes and some types of numbers generalized from the original definition of a Wieferich prime. Over time, those connections discovered have extended to cover more properties of certain prime numbers as well as more general subjects such as number fields and the abc conjecture. (Full article...) -
Image 5Mathematical economics is the application of mathematical methods to represent theories and analyze problems in economics. Often, these applied methods are beyond simple geometry, and may include differential and integral calculus, difference and differential equations, matrix algebra, mathematical programming, or other computational methods. Proponents of this approach claim that it allows the formulation of theoretical relationships with rigor, generality, and simplicity.
Mathematics allows economists to form meaningful, testable propositions about wide-ranging and complex subjects which could less easily be expressed informally. Further, the language of mathematics allows economists to make specific, positive claims about controversial or contentious subjects that would be impossible without mathematics. Much of economic theory is currently presented in terms of mathematical economic models, a set of stylized and simplified mathematical relationships asserted to clarify assumptions and implications. (Full article...) -
Image 6
James Clerk Maxwell FRS FRSE (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish physicist and mathematician who was responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and light as different manifestations of the same phenomenon. Maxwell's equations for electromagnetism achieved the second great unification in physics, where the first one had been realised by Isaac Newton. Maxwell was also key in the creation of statistical mechanics.
With the publication of "A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field" in 1865, Maxwell demonstrated that electric and magnetic fields travel through space as waves moving at the speed of light. He proposed that light is an undulation in the same medium that is the cause of electric and magnetic phenomena. The unification of light and electrical phenomena led to his prediction of the existence of radio waves, and the paper contained his final version of his equations, which he had been working on since 1856. As a result of his equations, and other contributions such as introducing an effective method to deal with network problems and linear conductors, he is regarded as a founder of the modern field of electrical engineering. In 1871, Maxwell became the first Cavendish Professor of Physics, serving until his death in 1879. (Full article...) -
Image 7

Hendrik Antoon Lorentz (right) after whom the Lorentz group is named and Albert Einstein whose special theory of relativity is the main source of application. Photo taken by Paul Ehrenfest 1921.
The Lorentz group is a Lie group of symmetries of the spacetime of special relativity. This group can be realized as a collection of matrices, linear transformations, or unitary operators on some Hilbert space; it has a variety of representations. This group is significant because special relativity together with quantum mechanics are the two physical theories that are most thoroughly established, and the conjunction of these two theories is the study of the infinite-dimensional unitary representations of the Lorentz group. These have both historical importance in mainstream physics, as well as connections to more speculative present-day theories. (Full article...) -
Image 8
The Laves graph
In geometry and crystallography, the Laves graph is an infinite and highly symmetric system of points and line segments in three-dimensional Euclidean space, forming a periodic graph. Three equal-length segments meet at 120° angles at each point, and all cycles use ten or more segments. It is the shortest possible triply periodic graph, relative to the volume of its fundamental domain. One arrangement of the Laves graph uses one out of every eight of the points in the integer lattice as its points, and connects all pairs of these points that are nearest neighbors, at distance. It can also be defined, divorced from its geometry, as an abstract undirected graph, a covering graph of the complete graph on four vertices.
H. S. M. Coxeter (1955) named this graph after Fritz Laves, who first wrote about it as a crystal structure in 1932. It has also been called the K4 crystal, (10,3)-a network, diamond twin, triamond, and the srs net. The regions of space nearest each vertex of the graph are congruent 17-sided polyhedra that tile space. Its edges lie on diagonals of the regular skew polyhedron, a surface with six squares meeting at each integer point of space. (Full article...) -
Image 9

YBC 7289
YBC 7289 is a Babylonian clay tablet notable for containing an accurate sexagesimal approximation to the square root of 2, the length of the diagonal of a unit square. This number is given to the equivalent of six decimal digits, "the greatest known computational accuracy ... in the ancient world". The tablet is believed to be the work of a student in southern Mesopotamia from some time between 1800 and 1600 BC. (Full article...) -
Image 10

A unit distance graph with 16 vertices and 40 edges
In mathematics, particularly geometric graph theory, a unit distance graph is a graph formed from a collection of points in the Euclidean plane by connecting two points whenever the distance between them is exactly one. To distinguish these graphs from a broader definition that allows some non-adjacent pairs of vertices to be at distance one, they may also be called strict unit distance graphs or faithful unit distance graphs. As a hereditary family of graphs, they can be characterized by forbidden induced subgraphs. The unit distance graphs include the cactus graphs, the matchstick graphs and penny graphs, and the hypercube graphs. The generalized Petersen graphs are non-strict unit distance graphs.
An unsolved problem of Paul Erdős asks how many edges a unit distance graph onvertices can have. The best known lower bound is slightly above linear in
—far from the upper bound, proportional to
. The number of colors required to color unit distance graphs is also unknown (the Hadwiger–Nelson problem): some unit distance graphs require five colors, and every unit distance graph can be colored with seven colors. For every algebraic number there is a unit distance graph with two vertices that must be that distance apart. According to the Beckman–Quarles theorem, the only plane transformations that preserve all unit distance graphs are the isometries. (Full article...)
-
Image 11

Kissing circles. Given three mutually tangent circles (black), there are, in general, two possible answers (red) as to what radius a fourth tangent circle can have.
In geometry, Descartes' theorem states that for every four kissing, or mutually tangent circles, the radii of the circles satisfy a certain quadratic equation. By solving this equation, one can construct a fourth circle tangent to three given, mutually tangent circles. The theorem is named after René Descartes, who stated it in 1643.
Frederick Soddy's 1936 poem The Kiss Precise summarizes the theorem in terms of the bends (signed inverse radii) of the four circles: (Full article...) -
Image 12

Partition of a directed graph into a minimum feedback arc set (red dashed edges) and a maximum acyclic subgraph (blue solid edges)
In graph theory and graph algorithms, a feedback arc set or feedback edge set in a directed graph is a subset of the edges of the graph that contains at least one edge out of every cycle in the graph. Removing these edges from the graph breaks all of the cycles, producing an acyclic subgraph of the given graph, often called a directed acyclic graph. A feedback arc set with the fewest possible edges is a minimum feedback arc set and its removal leaves a maximum acyclic subgraph; weighted versions of these optimization problems are also used. If a feedback arc set is minimal, meaning that removing any edge from it produces a subset that is not a feedback arc set, then it has an additional property: reversing all of its edges, rather than removing them, produces a directed acyclic graph.
Feedback arc sets have applications in circuit analysis, chemical engineering, deadlock resolution, ranked voting, ranking competitors in sporting events, mathematical psychology, ethology, and graph drawing. Finding minimum feedback arc sets and maximum acyclic subgraphs is NP-hard; it can be solved exactly in exponential time, or in fixed-parameter tractable time. In polynomial time, the minimum feedback arc set can be approximated to within a polylogarithmic approximation ratio, and maximum acyclic subgraphs can be approximated to within a constant factor. Both are hard to approximate closer than some constant factor, an inapproximability result that can be strengthened under the unique games conjecture. For tournament graphs, the minimum feedback arc set can be approximated more accurately, and for planar graphs both problems can be solved exactly in polynomial time. (Full article...)
Did you know
- ... that circle packings in the form of a Doyle spiral were used to model plant growth long before their mathematical investigation by Doyle?
- ... that despite published scholarship to the contrary, Andrew Planta neither received a doctorate nor taught mathematics at Erlangen?
- ... that in the aftermath of the American Civil War, the only Black-led organization providing teachers to formerly enslaved people was the African Civilization Society?
- ... that the British National Hospital Service Reserve trained volunteers to carry out first aid in the aftermath of a nuclear or chemical attack?
- ... that ten-sided gaming dice have kite-shaped faces?
- ... that despite a mathematical model deeming the ice cream bar flavour Goody Goody Gum Drops impossible, it was still created?
- ... that Ewa Ligocka cooked another mathematician's goose?
- ... that Catechumen, a Christian first-person shooter, was funded only in the aftermath of the Columbine High School massacre?

- ...that the six permutations of the vector (1,2,3) form a regular hexagon in 3d space, the 24 permutations of (1,2,3,4) form a truncated octahedron in four dimensions, and both are examples of permutohedra?
- ...that Ostomachion is a mathematical treatise attributed to Archimedes on a 14-piece tiling puzzle similar to tangram?
- ...that some functions can be written as an infinite sum of trigonometric polynomials and that this sum is called the Fourier series of that function?
- ...that the identity elements for arithmetic operations make use of the only two whole numbers that are neither composites nor prime numbers, 0 and 1?
- ...that as of April 2010 only 35 even numbers have been found that are not the sum of two primes which are each in a Twin Primes pair? ref
- ...the Piphilology record (memorizing digits of Pi) is 70000 as of Mar 2015?
- ...that people are significantly slower to identify the parity of zero than other whole numbers, regardless of age, language spoken, or whether the symbol or word for zero is used?
Showing 7 items out of 75
Featured pictures
-
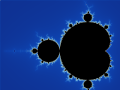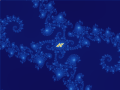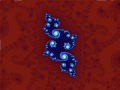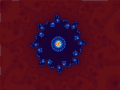
Image 1Mandelbrot set, step 8, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 2Fields Medal, back, by Stefan Zachow (edited by King of Hearts) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 4Hypotrochoid, by Sam Derbyshire (edited by Anevrisme and Perhelion) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 5Fields Medal, front, by Stefan Zachow (edited by King of Hearts) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 6Mandelbrot set, step 13, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 7Mandelbrot set, step 11, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 9Mandelbrot set, step 9, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 11Mandelbrot set, step 2, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 12Proof of the Pythagorean theorem, by Joaquim Alves Gaspar (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 13Mandelbrot set, step 3, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 14Mandelbrot set, step 12, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 15Cellular automata at Reflector (cellular automaton), by Simpsons contributor (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 16Mandelbrot set, step 14, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 17Mandelbrot set, step 7, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
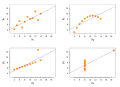
Image 18Anscombe's quartet, by Schutz (edited by Avenue) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 19Mandelbrot set, start, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 20Mandelbrot set, step 1, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 21Lorenz attractor at Chaos theory, by Wikimol (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 22Mandelbrot set, step 10, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 23Line integral of scalar field, by Lucas V. Barbosa (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 24Non-uniform rational B-spline, by Greg L (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 25Mandelbrot set, step 5, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 27Mandelbrot set, by Simpsons contributor (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 28Tetrahedral group at Symmetry group, by Debivort (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 29Desargues' theorem, by Dynablast (edited by Jujutacular and Julia W) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 32Mandelbrot set, step 4, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 34Mandelbrot set, step 6, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
Get involved
- For editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Mathematics-related articles, visit WikiProject Mathematics.
Categories
Topics
Index of articles
| ARTICLE INDEX: | |
| MATHEMATICIANS: |
Vital articles
- » subpages: Level 4 Mathematics articles, Level 5 Mathematics articles
Discover Wikipedia using portals
Hidden categories:
- Pages using the Phonos extension
- Pages including recorded pronunciations
- Pages with German IPA
- Pages with Swiss Standard German IPA
- Wikipedia semi-protected portals
- Manually maintained portal pages from December 2018
- All manually maintained portal pages
- Portals with triaged subpages from December 2018
- All portals with triaged subpages
- Portals with named maintainer
- Wikipedia move-protected portals
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 31–40 articles in article list
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 101–200 articles in article list
- Random portal component with over 50 available subpages